二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树的算法运行时间取决于树的形状,而树的形状又取决于键被插入的先后顺序。在最好的情况下,一颗含有N个节点的树是完全平衡的,每条空链接和 根节点的距离都为~lgN。在最坏的情况下,搜索路径上可能有N个节点
1979年J.Robson证明了随机键构造的二叉搜索树的平均高度为树中节点数的对数级别,随后L.Devroye证明了对于N足够大的情况下,平均高度趋近于2.99lgN。
也就是说树的构造和随机模型近似时在各种应用场景中它都能进行快速的插入和查找,但是构造树的键不够随机时可能导致最坏情况出现,二叉搜索树在最坏情况下 的性能是不能接受的。所以二叉搜索树的基本良好性能依赖于其中的键的分布足够随机
下面列出了二分查找和二叉树查找成本:
| 算法 | 最坏情况下运行时间的增长数量级(N次插入后)查找操作 | 最坏情况下运行时间的增长数量级(N次插入后)插入操作 | 平均情况下运行时间的增长数量级(N次插入后)查找操作 | 平均情况下运行时间的增长数量级(N次插入后)插入操作 | 有序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 二分查找(有序数组) | lgN | N | lgN | N/2 | 是 |
| 二叉树查找(二叉搜索树) | N | N | 1.39lgN | 1.39lgN | 是 |
二叉搜索树实现
二叉搜索树的实现需提供以下基础API:
- 插入Put
- 查找Get
- 前序遍历PreOrderWithRecursion
- 中序遍历MiddleOrderWithRecursion
- 后序遍历LastOrderWithRecursion
- 删除Delete
- 树的高度Height
- 删除最大键DelMax
- 删除最小键DelMin
- 最小键Min
- 最大键Max
- 向上取整Ceiling
- 向下取整Floor
- 根据排名获取键Select
- 根据键获取排名Rank
具体实现代码可以参考github上的代码
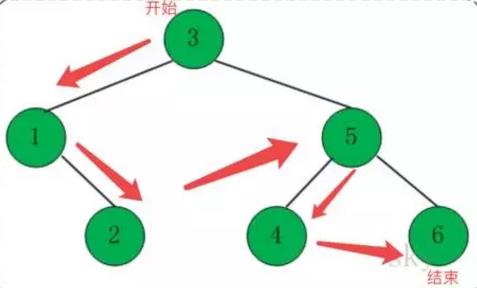
前序遍历
前序遍历过程分为以下几步:
-
访问根节点
-
前序遍历左子树
-
前序遍历右子树
遍历过程如下图:
递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void PreOrderWithRecursion(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)const noexcept
{
if (nullptr == node)
{
return;
}
fun(node->val);
PreOrderWithRecursion(node->left.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
PreOrderWithRecursion(node->right.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
}
非递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void PreOrderWithStack(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)
{
if (nullptr == node)
{
return;
}
std::stack<NodeType*> node_stack;
while (node != nullptr || !node_stack.empty())
{
if (node != nullptr)
{
fun(node->val);
node_stack.push(node);
node = node->left.get();
}
else
{
node = node_stack.top();
node_stack.pop();
node = node->right.get();
}
}
}
中序遍历
中序遍历过程分为以下几步:
-
中序遍历左子树
-
访问根节点
-
中序遍历右子树
遍历过程如下图:
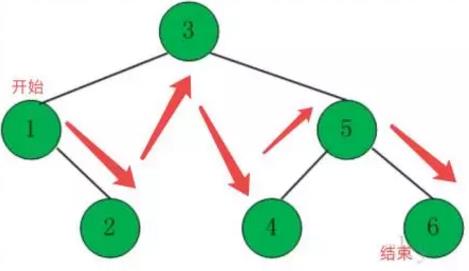
对一个二叉搜索树进行中序遍历是一种按数据大小的顺序遍历
递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void MiddleOrderWithRecursion(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)const noexcept
{
if (nullptr == node)
{
return;
}
MiddleOrderWithRecursion(node->left.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
fun(node->val);
MiddleOrderWithRecursion(node->right.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
}
非递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void MiddleOrderWithStack(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)
{
if (nullptr == node)
{
return;
}
std::stack<NodeType*> node_stack;
while (nullptr != node || !node_stack.empty())
{
if (nullptr != node)
{
node_stack.push(node);
node = node->left.get();
}
else
{
node = node_stack.top();
fun(node->val);
node_stack.pop();
node = node->right.get();
}
}
}
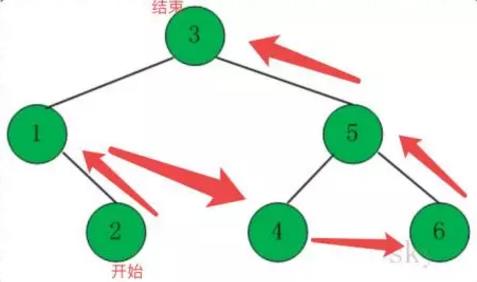
后序遍历
后序遍历过程分为以下几步:
-
后序遍历左子树
-
后序遍历右子树
-
访问根节点
遍历过程如下图:
递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void LastOrderWithRecursion(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)const noexcept
{
if (nullptr == pRoot)
{
return;
}
LastOrderWithRecursion(node->left.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
LastOrderWithRecursion(node->right.get(), std::forward<TTraversingCb>(fun));
fun(node->val);
}
非递归实现:
template<typename TTraversingCb>
void LastOrderWithStack(NodeType* node, TTraversingCb&& fun)
{
if (nullptr == node)
{
return;
}
std::stack<NodeType*> tmp_stack,out_stack;
tmp_stack.push(node);
while (!tmp_stack.empty())
{
NodeType* curr = tmp_stack.top();
out_stack.push(curr);
tmp_stack.pop();
if (curr->left.get())
{
tmp_stack.push(curr->left.get());
}
if (curr->right.get())
{
tmp_stack.push(curr->right.get());
}
}
while (!out_stack.empty())
{
fun(out_stack.top()->val);
out_stack.pop();
}
}